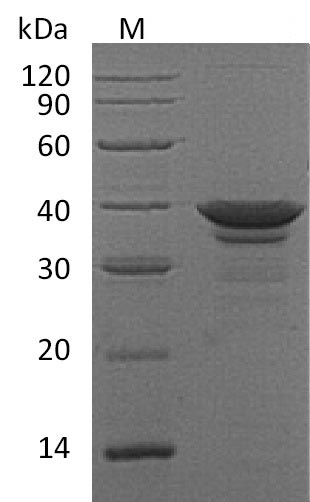
The human Arginase-1 (ARG1) protein's gene (1-322aa) is co-inserted into a plasmid vector with the C-terminal 6xHis-tag gene, forming a recombinant plasmid, which is introduced into E.coli cells. E.coli cells surviving in the presence of a specific antibiotic are selected and then cultured under conditions promoting the expression of the target gene. After expression, the recombinant human ARG1 protein is isolated and purified from the cell lysate through affinity purification. Denaturing SDS-PAGE is utilized to resolve the resulting recombinant ARG1 protein, revealing a purity exceeding 95%. The endotoxin content of this protein is less than 1.0 EU/μg as determined by the LAL method. Its specific activity is greater than 6000 pmol/min/ug as determined through the generation of urea during the hydrolysis of arginine.
ARG1, also known as arginase 1, is a key enzyme in various body processes. It comes in two forms, ARG1 (found in the cell's liquid part) and ARG2 (found in the mitochondria), and shows up in different cell types, like lung blood vessel cells [1]. When dealing with infections from certain pathogens like Schistosoma mansoni, ARG1 in specific immune cells called macrophages acts as a brake on inflammation and scarring [2]. These immune cells produce more ARG1 when they receive signals from nearby cells, especially when triggered by substances like IL-4 or IL-13 during certain immune responses [3]. In artery plaques associated with heart disease, ARG1 mostly hangs out in macrophages and other nearby cells, not the ones surrounding the fatty core of the plaque [4].
ARG1 also gets involved in how plants sense and respond to gravity, possibly by tweaking the activity or location of proteins involved in sensing gravity [5]. It also slows down the growth of certain immune cells by breaking down a molecule called arginine outside the cells, making the immune cells less responsive to certain signals [6]. It's a big deal in macrophage biology, often used as a marker for a particular type of macrophage activity [7]. In tuberculosis, when another enzyme called NOS2 can't do its job because of low oxygen levels, ARG1 steps in to help control the infection [8]. Plus, it's a key player in making ornithine, an important part of a pathway that controls cell growth [9].
In neurodegenerative diseases, keeping arginine metabolism in check through ARG1 is crucial for certain brain cells to do their job properly, and messing up this balance can mess up their functions [10]. In tuberculosis patients, ARG1 shows up in certain immune cells and lung cells associated with the disease [11].
References:
[1] R. Lucas, I. Czikora, S. Sridhar, E. Zemskov, A. Oseghale, S. Circoet al., Arginase 1: an unexpected mediator of pulmonary capillary barrier dysfunction in models of acute lung injury, Frontiers in Immunology, vol. 4, 2013. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00228
[2] J. Pesce, T. Ramalingam, M. Mentink‐Kane, M. Wilson, K. Kasmi, A. Smithet al., Arginase-1–expressing macrophages suppress th2 cytokine–driven inflammation and fibrosis, Plos Pathogens, vol. 5, no. 4, p. e1000371, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000371
[3] J. Qualls, G. Neale, A. Smith, M. Koo, A. DeFreitas, H. Zhanget al., Arginine usage in mycobacteria-infected macrophages depends on autocrine-paracrine cytokine signaling, Science Signaling, vol. 3, no. 135, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2000955
[4] B. Pourcet, J. Feig, Y. Vengrenyuk, A. Hobbs, D. Kepka‐Lenhart, M. Garabedianet al., Lxrα regulates macrophage arginase 1 through pu.1 and interferon regulatory factor 8, Circulation Research, vol. 109, no. 5, p. 492-501, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.111.241810
[5] B. Harrison and P. Masson, Arl2, arg1 and pin3 define a gravity signal transduction pathway in root statocytes, The Plant Journal, vol. 53, no. 2, p. 380-392, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313x.2007.03351.x
[6] R. Rotondo, G. Barisione, L. Mastracci, F. Grossi, A. Orengo, R. Costaet al., Il‐8 induces exocytosis of arginase 1 by neutrophil polymorphonuclears in nonsmall cell lung cancer, International Journal of Cancer, vol. 125, no. 4, p. 887-893, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24448
[7] Y. Fu, J. Wang, B. Zhou, A. Pajulas, H. Gao, B. Ramdaset al., An il-9–pulmonary macrophage axis defines the allergic lung inflammatory environment, Science Immunology, vol. 7, no. 68, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.abi9768
[8] M. Duque-Correa, A. Kühl, P. Rodríguez, U. Zedler, S. Schommer-Leitner, M. Raoet al., Macrophage arginase-1 controls bacterial growth and pathology in hypoxic tuberculosis granulomas, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 111, no. 38, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1408839111
[9] Y. Yang, M. Song, Y. Li, F. He, W. Chao, M. Chenet al., The role of the complement factor b‒arginase‒polyamine molecular axis in uremia‐induced cardiac remodeling in mice, European Journal of Immunology, vol. 50, no. 2, p. 220-233, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201948227
[10] M. C, J. Hunt, A. Kovalenko, H. Liu, M. Selenica, M. Orret al., Myeloid arginase 1 insufficiency exacerbates amyloid-β associated neurodegenerative pathways and glial signatures in a mouse model of alzheimer’s disease: a targeted transcriptome analysis, Frontiers in Immunology, vol. 12, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.628156
[11] A. Pessanha, R. Martins, A. Mattos‐Guaraldi, A. Vianna, & L. Moreira, Arginase-1 expression in granulomas of tuberculosis patients: figure 1, Fems Immunology & Medical Microbiology, vol. 66, no. 2, p. 265-268, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695x.2012.01012.x"