World Down Syndrome Day: Exploring and Caring Never Ceases in the Complex "Chromosome Challenge" of Humanity
March 21, 2024, marks the 13th World Down Syndrome Day. Down Syndrome (DS), also known as trisomy 21, is a common chromosomal anomaly in humans, characterized by an abnormality in the number of chromosomes, particularly chromosome 21. Individuals with Down Syndrome often exhibit congenital intellectual disability, developmental delays, distinctive facial features, congenital heart disease, acute leukemia, congenital gastrointestinal anomalies, and Alzheimer's disease, among other severe clinical conditions.
As early as about 2500 years ago in the pottery art of the Tumaco-La Tolita culture, Bernal et al. discovered depictions of characters with typical DS features. However, in earlier times, understanding of DS was confused with cretinism, a condition associated with thyroid dysfunction, mistakenly believed to be a form of intellectual disability caused by thyroid deficiency. Yet, with the widespread application of thyroid treatment in DS and cretinism children by the late 1950s, it was found that such therapy had little significant effect on most DS children. Meanwhile, with improvements in socioeconomic conditions and nutritional status, the incidence of cretinism gradually declined, leading to a clearer understanding of DS as a distinct condition apart from thyroid dysfunction.
Despite the complex mechanisms underlying DS and the lack of a cure currently, researchers have never ceased their exploration of the disease. Now, let us delve into recent scientific research advancements to gain a deeper understanding of the research achievements in Down Syndrome in recent years and potential future therapeutic directions.
Science Translational Medicine: Increased dosage of DYRK1A leads to congenital heart defects in a mouse model of Down syndrome [1]
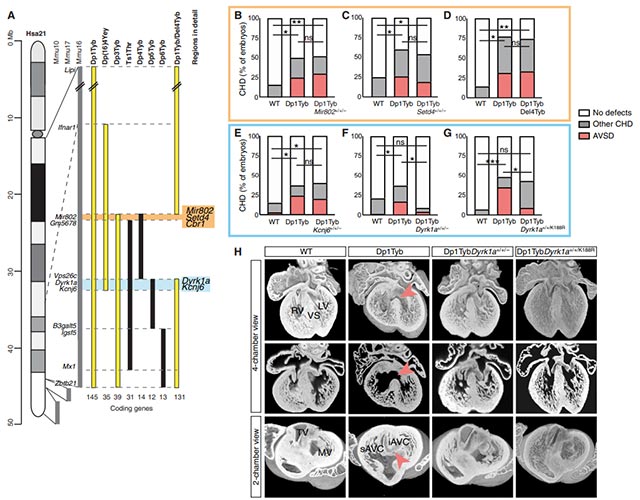
Down Syndrome (DS) is caused by an extra copy of human chromosome 21 (Hsa21), leading to various characteristics including congenital heart defects. In a recent study, researchers analyzed transcriptomic data from both human fetal hearts with DS and mouse embryo hearts mimicking DS. They found a link between reduced expression of mitochondrial respiratory genes and cell proliferation genes and the development of congenital heart disease (CHD). By genetic mapping, they identified Dyrk1a as one of the genes responsible for CHD in DS. Increased Dyrk1a dosage impairs cell proliferation and disrupts mitochondrial function, indicating it as a potential target for treating CHD in DS.
Fig.1. Three copies of Dyrkla are necessary to cause heart defects. [1]
Neurochemistry International: Early chronic fasudil treatment rescues hippocampal alterations in the Ts65Dn model for down syndrome [2]
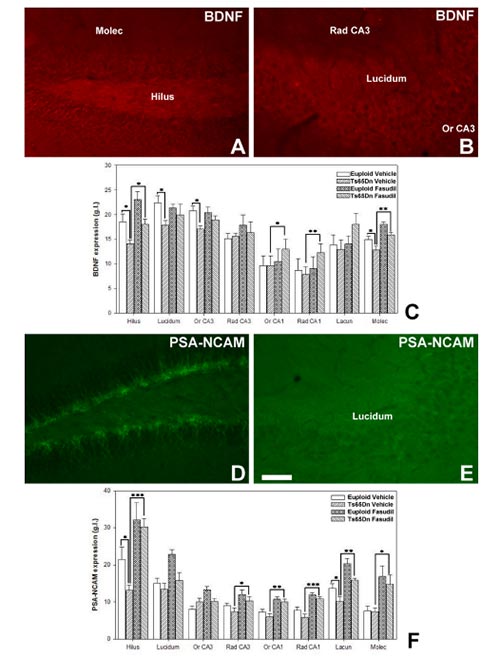
Down Syndrome (DS) is a common genetic disorder linked to intellectual disabilities. Scientists use mouse models like Ts65Dn to study DS, which mirrors many DS traits, including brain abnormalities. In a recent study, researchers treated Ts65Dn mice with Fasudil, a drug targeting dendritic spine formation. After 28 days of treatment, they found improved dendritic structure and molecular markers related to brain plasticity. This suggests Fasudil could correct some DS-related neural defects, offering a new therapeutic approach.
Fig.2. Changes in neuroplastic molecules expression in the hippocampus after chronic treatment with fasudil [2]
Science: GnRH replacement rescues cognition in Down syndrome [3]
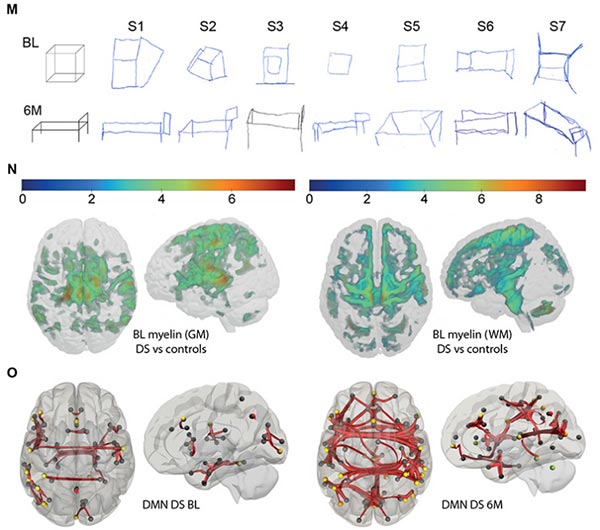
Currently, effective treatments for cognitive and olfactory deficits in Down Syndrome (DS) are lacking. In a study using a DS model (Ts65Dn mice), researchers found that the progressively worsening non-reproductive system neurological symptoms were closely associated with decreased expression of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), a key molecule regulating reproduction in the hypothalamus and extrahypothalamic areas post-puberty. These symptoms also appeared to be related to an imbalance in a microRNA-gene network known to regulate GnRH neuron maturation and hippocampal synaptic transmission changes. Restoring physiological levels of GnRH through epigenetics, cell biology, chemical genetics, and drug intervention can eliminate olfactory and cognitive deficits in Ts65Dn mice. Moreover, pulse GnRH therapy has the potential to improve cognitive function and brain connectivity in adult DS patients. Thus, GnRH plays a crucial role in olfaction and cognition, and pulse GnRH therapy holds promise for improving cognitive deficits in DS patients.
Fig.3. Pulsatile GnRH improves patient brain connectivity, cognition [3]
Nature: Autoimmunity in Down’s syndrome via cytokines, CD4 T cells and CD11c+ B cells [4]
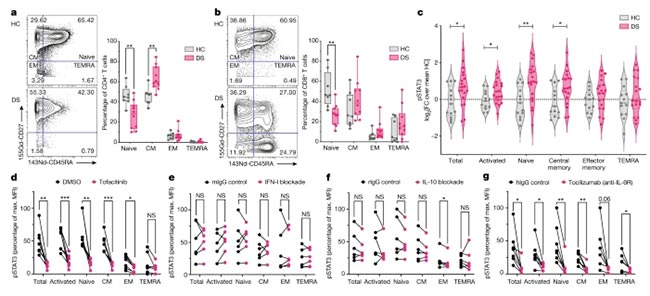
Researchers studied the immune system of Down Syndrome (DS) patients and found consistently high levels of certain cytokines, along with abnormal activation of immune cells. Specifically, chronic IL-6 signaling in CD4 T cells and increased autoimmunity-prone B cell subsets were observed. These factors may lead to excessive production of autoantibodies targeting various organs. In vitro experiments confirmed that plasma from DS patients and IL-6-activated T cells could exacerbate autoimmune responses by promoting B cell differentiation into plasma cells. Importantly, both traditional Jak inhibitors and targeted IL-6 inhibition were effective in regulating immune responses in DS patients, suggesting new treatment avenues for DS-related autoimmune issues.
Fig.4. T cell activation in DS is rescued by Jak inhibition or IL-6 blockade [4]
Brain: Prenatal pharmacotherapy rescues brain development in a Down's syndrome mouse model [5]
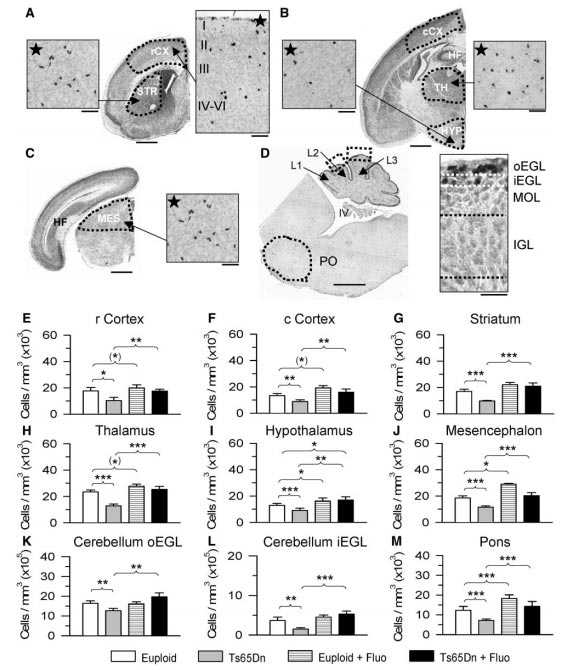
For a long time, cognitive issues in Down syndrome were seen as irreversible. This study explores if prenatal fluoxetine treatment can reverse characteristic brain abnormalities in Down syndrome. Pregnant Ts65Dn mice received fluoxetine from day 10 of gestation until birth. Results suggest fluoxetine during pregnancy can fully reverse abnormal brain development and behavior linked to Down syndrome. If these findings extend to human fetuses, fluoxetine could be a breakthrough treatment for Down syndrome-related cognitive impairments.
Fig.5. Effect of embryonictreatment with fluoxetineon precursor proliferation in different brain regions [5]
On March 21st, World Down Syndrome Day serves not only to raise awareness about this chromosomal disorder but also to convey a resolute message: in the face of this seemingly insurmountable human "chromosome challenge," we have never ceased our pursuit of understanding! For years, researchers have tirelessly delved into the disease mechanisms behind Down syndrome, striving to unravel its intricate connections with cognitive impairments and physiological developmental issues.
CUSABIO has long been committed to providing high-quality research tools such as proteins, antibodies, and ELISA assay kits for researchers. We have curated a list of 20 popular research targets and related assay products related to Down syndrome research, as follows, for your consideration:
DS Research Hot Target ELISA Kits:
DS Research Hot Target Recombinant Proteins:
| Product Name |
Code |
Target |
Source |
Tag Info |
| Recombinant Human Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), partial (Active) |
CSB-AP005671HU |
ACE2 |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| Recombinant Human Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), partial, Biotinylated (Active) |
CSB-MP866317HU-B |
ACE2 |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal mFc-Avi-tagged |
| Recombinant Human Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), partial (Active) |
CSB-MP866317HU |
ACE2 |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal hFc-tagged |
| Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE2), partial (Active) |
CSB-MP3414MOV |
ACE2 |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal hFc-tagged |
| Recombinant Paguma larvata Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), partial (Active) |
CSB-MP684964PAL |
ACE2 |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal hFc-tagged |
| Recombinant Mesocricetus auratus Angiotensin-converting enzyme (Ace2), partial |
CSB-EP4885MRG |
Ace2 |
E.coli |
N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Strep II-tagged |
| Recombinant Human RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1) |
CSB-EP001553HU |
AKT1 |
E.coli |
N-terminal GST-tagged |
| Recombinant Rat RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (Akt1) |
CSB-EP001553RA |
Akt1 |
E.coli |
N-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| Recombinant Mouse Apolipoprotein E (Apoe) |
CSB-BP001936MO |
Apoe |
Baculovirus |
N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged |
| Recombinant Mouse Apolipoprotein E (Apoe) |
CSB-EP001936MO |
Apoe |
E.coli |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| Recombinant Rabbit Apolipoprotein E (APOE), partial |
CSB-EP001936RB |
APOE |
E.coli |
N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged |
| Recombinant Rabbit Apolipoprotein E (APOE), partial |
CSB-EP001936RBb3 |
APOE |
E.coli |
N-terminal 10xHis-SUMO-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged |
| Recombinant Rabbit Apolipoprotein E (APOE), partial |
CSB-EP001936RBb7 |
APOE |
E.coli |
N-terminal 10xHis-B2M-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged |
| Recombinant Mouse Apolipoprotein E (Apoe) |
CSB-MP001936MO |
Apoe |
Mammalian cell |
N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged |
| Recombinant Mouse Apolipoprotein E (Apoe) |
CSB-YP001936MO |
Apoe |
Yeast |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| Recombinant Mouse Apolipoprotein E (Apoe) |
CSB-EP001936MOc7 |
Apoe |
E.coli |
C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| Recombinant Dog Apolipoprotein E (APOE) |
CSB-EP001936DO |
APOE |
E.coli |
N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged |
| Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Apolipoprotein E (APOE) |
CSB-EP001936MOV |
APOE |
E.coli |
N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged |
| Recombinant Rat Apolipoprotein E (Apoe) |
CSB-EP001936RA |
Apoe |
E.coli |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| Recombinant Mouse Amyloid beta A4 protein (App) |
CSB-EP001950MOc7 |
App |
E.coli |
C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
DS Research Hot Target Antibodies:
● Recombinant Antibody
| Product Name |
Code |
Target |
Species Reactivity |
Tested Applications |
| Phospho-AKT1 (T450) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA001553A450phHU |
AKT1 |
Human |
ELISA, WB |
| Phospho-AKT1 (Ser473) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA001553A473phHU |
AKT1 |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, IP |
| AKT1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA917625A0HU |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| APP Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA994273A0HU |
APP |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IF |
| CD4 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA004935A0HU |
CD4 |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| CRP Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA988767A0HU |
CRP |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
| GAPDH Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA009232A0HU |
GAPDH |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB |
| GAPDH Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA009232MA1HU |
GAPDH |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC |
| IL10 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA011580A0HU |
IL10 |
Human |
ELISA |
| IL6 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA011664MA1HU |
IL6 |
Human |
ELISA |
| INS Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA584163A0HU |
INS |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
| Phospho-MAPT (T231) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA013481A231phHU |
MAPT |
Human |
ELISA, WB |
| Phospho-MAPT (S396) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA013481A396phHU |
MAPT |
Human |
ELISA, WB |
| Phospho-MAPT (S324) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA013481A324phHU |
MAPT |
Human |
ELISA, IF |
| MAPT Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA246354A0HU |
MAPT |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
| MAPT Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA013481A1HU |
MAPT |
Mouse, Macaca mulatta |
ELISA |
| Phospho-MAPT (S199) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA051594A0HU |
MAPT |
Human |
ELISA, IHC, FC |
| Phospho-MAPT (S404) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA901354A0HU |
MAPT |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
| Phospho-MAPT (S214) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA050476A0HU |
MAPT |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
| Phospho-MAPT (S202) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA082445A0HU |
MAPT |
Human |
ELISA, FC |
| MAPT Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA013481MA1HU |
MAPT |
Human |
ELISA, FC |
| Phospho-MTOR (S2481) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA008968A2481phHU |
MTOR |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IF |
| Phospho-MTOR (S2448) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA008968A2448phHU |
MTOR |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| Phospho-TP53 (T55) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA024077A55phHU |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IF |
| Phospho-TP53 (S392) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA024077A392phHU |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, WB |
| Phospho-TP53 (S33) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA024077A33phHU |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Phospho-TP53 (S9) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA024077A09phHU |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, IF |
| TP53 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA236796A0HU |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| TP53 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA825742A0HU |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| TP53 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA214807A0HU |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
| TP53 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA592348A0HU |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, IF |
| TP53 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-RA024077MA1HU |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IF, FC |
● Monoclonal Antibody
| Product Name |
Code |
Target |
Species Reactivity |
Tested Applications |
| AKT1 Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA011037 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Pig, Rat |
ELISA, WB |
| APP Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA0019501A0m |
APP |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| CD4 Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA000228 |
CD4 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, IHC |
| CD4 Monoclonal Antibody,Purified |
CSB-MA783233 |
CD4 |
Human |
ELISA, FC |
| CRP Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA027411E0m |
CRP |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
| GAPDH Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA000071M0m |
GAPDH |
Human, Rat, Rabbit |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP, IF, FC |
| GAPDH Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA000071M1m |
GAPDH |
Human, Mouse, Rabbit |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP, IF |
| GAPDH Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA000071M2m |
GAPDH |
Human, Rat, Rabbit, Mouse |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IP, IF |
| GAPDH Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA000184 |
GAPDH |
Human, Rat, Mouse, Monkey, Dog, Chicken, Hamster, Rabbit, Pig, Sheep, Insect, Yeast |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| GAPDH Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA000195 |
GAPDH |
Human, Rat, Mouse, Monkey, Dog, Chicken, Hamster, Rabbit, Pig, Sheep |
ELISA, WB |
| GAPDH Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA072309 |
GAPDH |
Human, Pig, Rat, Mouse |
ELISA, WB |
| IFNG Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA065241A0m |
IFNG |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
| IL6 Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA067571A0m |
IL6 |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| TNF Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA084771A0m |
TNF |
Bovine |
ELISA |
| TNF Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA080271 |
TNF |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| TNF Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA080272 |
TNF |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| TP53 Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA0240771A0m |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| TP53 Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA000208 |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| TP53 Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA989534 |
TP53 |
Human |
ELISA, WB |
| TP53 Monoclonal Antibody |
CSB-MA189580 |
TP53 |
Human, Dog, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB |
● Polyclonal Antibody
| Product Name |
Code |
Target |
Species Reactivity |
Tested Applications |
| ACE2 Antibody |
CSB-PA866317LA01HU |
ACE2 |
Human |
ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Ace2 Antibody |
CSB-PA688690OA01RA |
Ace2 |
Rat |
ELISA, WB |
| ACE2 Antibody |
CSB-PA040178 |
ACE2 |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB |
| ACE2 Antibody |
CSB-PA001150GA01HU |
ACE2 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB |
| ACE2 Antibody |
CSB-PA111496 |
ACE2 |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
| ACE2 Antibody |
CSB-PA025395 |
ACE2 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, IHC |
| ACE2 Antibody |
CSB-PA445794 |
ACE2 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, IHC |
| AKT1 Antibody |
CSB-PA15905A0Rb |
AKT1 |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, IP |
| AKT1 Antibody |
CSB-PA000852 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| Phospho-AKT1 (S124) Antibody |
CSB-PA008118 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| Phospho-AKT1 (T72) Antibody |
CSB-PA008120 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| AKT1 Antibody |
CSB-PA008122 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, IHC |
| AKT1 Antibody |
CSB-PA080256 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
WB |
| Phospho-AKT1 (S129) Antibody |
CSB-PA000645 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB |
| Phospho-AKT1 (T308) Antibody |
CSB-PA000657 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB |
| Phospho-AKT1 (S473) Antibody |
CSB-PA000732 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| AKT1 Antibody |
CSB-PA000851 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| Phospho-AKT1 (S246) Antibody |
CSB-PA000465 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| Phospho-AKT1 (T450) Antibody |
CSB-PA000468 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
| Phospho-AKT1 (Y326) Antibody |
CSB-PA000649 |
AKT1 |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB |
References:
[1] Increased dosage of DYRK1A leads to congenital heart defects in a mouse model of Down syndrome[J].EVA LANA-ELOLA, RIFDAT AOIDI. et al. SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE. 24 Jan 2024.
[2] Early chronic fasudil treatment rescues hippocampal alterations in the Ts65Dn model for down syndrome[J]. Rosa Lopez-Hidalgo, Raul Ballestin, et al. Neurochemistry International. Volume 174, March 2024.
[3] GnRH replacement rescues cognition in Down syndrome[J].MARIA MANFREDI-LOZANO, VALERIE LEYSEN, MICHELA ADAMO, et al. Science.2 Sep 2022 : Vol 377.
[4] Autoimmunity in Down's syndrome via cytokines, CD4 T cells and CD11c+ B cells[J]. Louise Malle, Roosheel S. Patel. et al. Nature 615, 305-314 (2023).
[5] Prenatal pharmacotherapy rescues brain development in a Down's syndrome mouse model[J].Sandra Guidi, Fiorenza Stagni. et al. Brain. 2014 Feb;137(Pt 2):380-401.